Understanding The Battery Charging Modes: Constant Current and Constant Voltage Modes
Charging is the process of replenishing the battery energy in a controlled manner. To charge a battery, a DC power source with a voltage higher than the battery, along with a current regulation mechanism, is required. To ensure the efficient and safe charging of batteries, it is crucial to understand the various charging modes. Two distinct modes are available for battery charging, each catering to specific needs within the charging process:
- Constant Current Mode (CC Mode): As the name implies, in this mode, the charging current for the battery is maintained at a constant value by adjusting the output voltage of the DC power source.
- Constant Voltage Mode (CV Mode): In this mode, the charging voltage applied at the battery terminals is maintained constant regardless of the battery charging current.
Let’s examine these charging modes within the context of EV charging. The illustration below provides a simplified depiction of the EV charging system to facilitate an understanding of the charging modes.
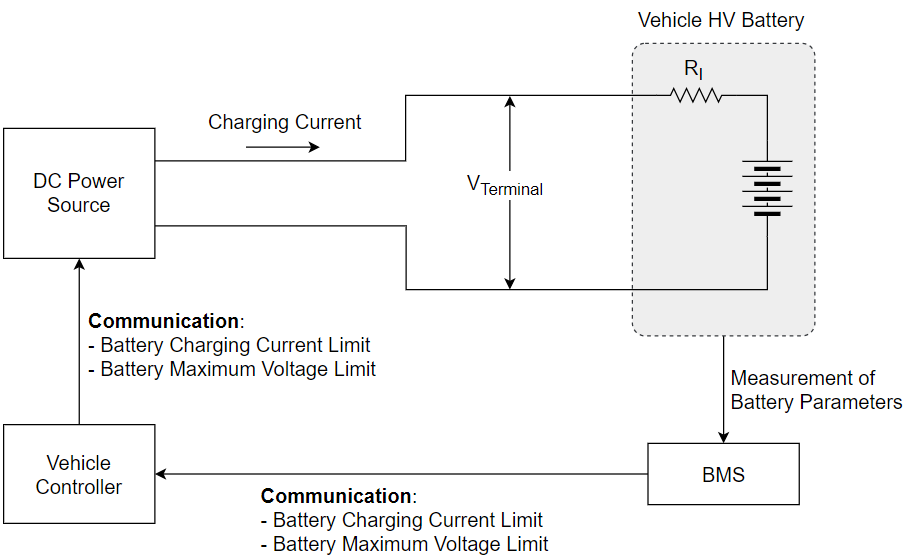
Here,
BMS = Battery Management System
DC Power Source = OBC or DC charging station
VTerminal = Terminal voltage which could be Charging voltage or Battery voltage
RI = Internal resistance of the battery. It is the lumpsum of all the individual cells’ internal resistances
To gain a deeper insight into the charging modes, it is essential to understand the battery charging profile. The following example illustrates the battery charging profile, where the battery exhibits a step profile for the charging current limit. As the State of Charge (SOC) increases, the battery charging current limit decreases in steps. Additionally, we observe that the battery voltage increases linearly with SOC.
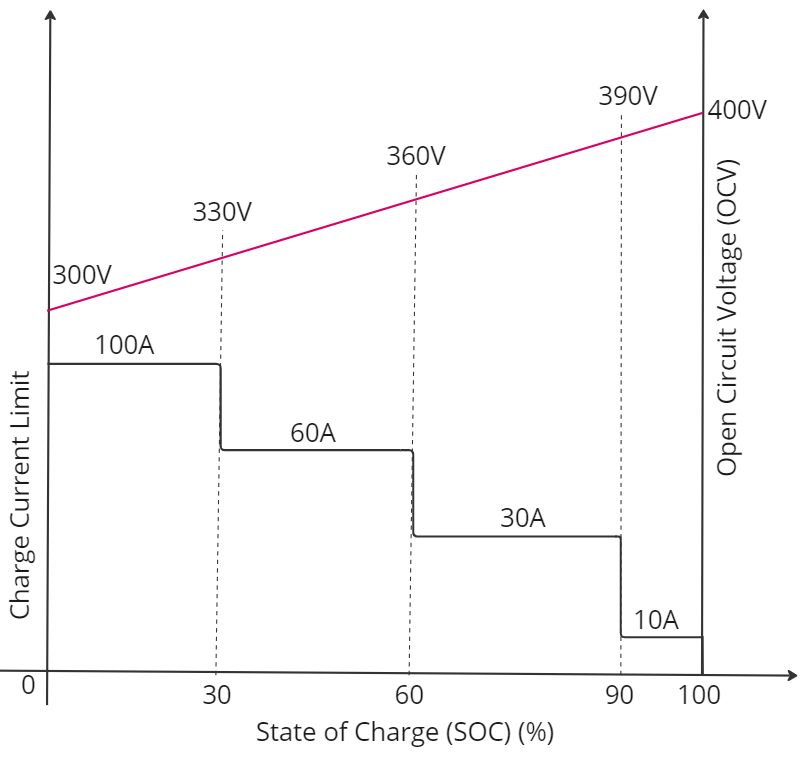
Here,
Open Circuit Voltage (OCV) = VTerminal when no load is connected to the battery.
Battery Maximum Voltage Limit = OCV at the 100% SOC (full charge) = 400 V.
RI = Internal resistance of the battery = 0.2 Ohm
Note: The internal resistance and charging profile provided here is exclusively intended for understanding the CC and CV modes. The actual charging profile in EVs may differ from the representation provided here.
1. CC Mode:
CC Mode in electric vehicles refers to the process of charging the battery in accordance with the specified battery charge current limit. Contrary to the term, the charging current is not uniformly constant throughout the entire CC mode but adheres to the battery charge current limit determined by the BMS. The BMS calculates the maximum charging current limit and the maximum battery voltage limit, providing this information to the vehicle controller.
Subsequently, the vehicle controller communicates this data to the DC power source, which, in turn, adjusts its output voltage to attain the communicated charging current limit. Importantly, the DC power source ensures that it does not exceed the maximum battery voltage limit during this adjustment.
The relationship between the charging voltage and the battery charging current limit can be expressed by the formula:
Charging voltage = OCV + (RI x Battery charging current limit)
Here, RI is considered as 0.2 Ohm.
Observing the below picture, it becomes evident that the DC power source regulates its charging voltage in accordance with the charging current limit. Notably, as the SOC approaches towards 90%, the charging voltage reaches 400V which is the maximum battery voltage limit. This marks the end of the CC mode.
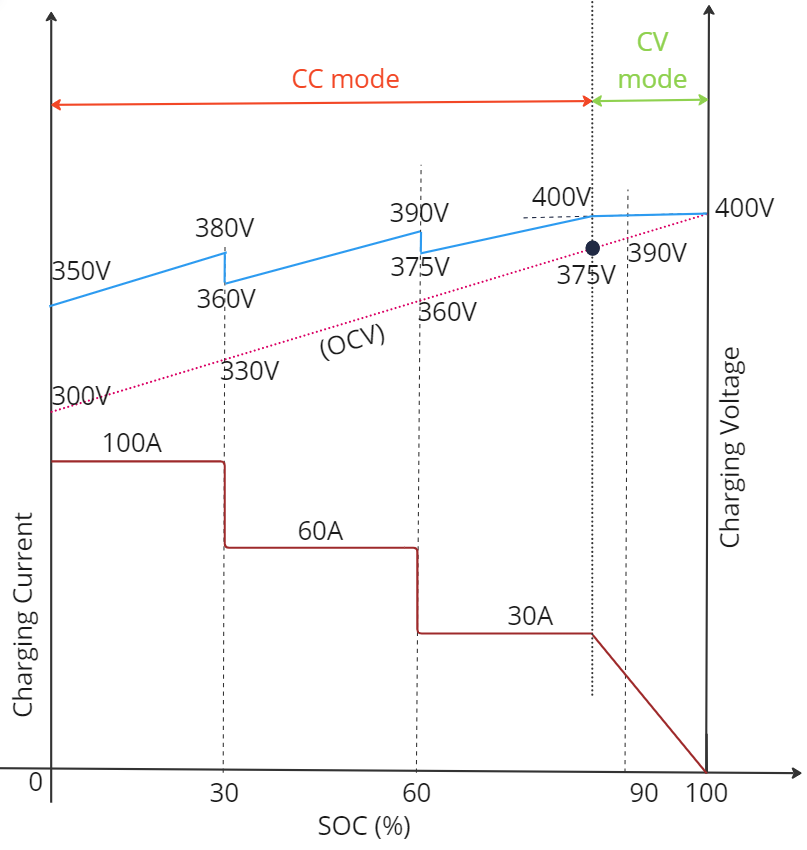
The significance of CC mode lies in its ability to rapidly charge the battery to higher SOC levels without violating the specified battery limits. This mode optimizes charging speed while maintaining the integrity and safety of the battery.
2. CV Mode:
End of the CC mode marks the beginning of CV mode in the charging process. Within the CV mode, the charging voltage is maintained at the maximum battery voltage limit (It can be seen in the above picture). Consequently, the charging current undergoes a gradual reduction as the SOC increases in the battery, ultimately leading to a longer duration to achieve 100% SOC.
This mode ensures that charging voltage is not exceeding the battery maximum voltage limit, a measure put in place to safeguard against potential over charge and chemical damages of the battery.
In essence, the orchestrated combination of CC and CV modes not only facilitates efficient charging but also safeguards the longevity and health of electric vehicle batteries.
EV Charging Explained – Everything you need to know about Electric Vehicle Charging