HVIL Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to HVIL in EVs
What is HVIL?
HVIL stands for High-Voltage Interlock Loop, a critical safety feature found in all electric vehicles (EVs). It is designed to protect individuals during the assembly, repair, maintenance, and operation of a vehicle by preventing accidental contact with high-voltage (HV) components. The HVIL system safeguards anyone who might interact with these components throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
When is it necessary?
HVIL becomes essential when dealing with HV systems. For systems operating within the range of >30V AC or >60V DC, HVIL is crucial due to the potential hazards of HV contact. Conversely, in low voltage systems, HVIL is not required. Gas-powered vehicles, which utilize electrical systems at lower voltages (12V-24V), do not necessitate HVIL, as they pose no risk to operators and service technicians. However, hybrid and EVs incorporate battery subsystems, wires, adapters, and controllers that operate at HV, necessitating the implementation of additional safety measures like HVIL.
How does it work?
The HVIL mechanism employs a continuous, low-voltage loop to monitor all HV connectors and components within an EV. An interruption in the low-voltage HVIL signal suggests a disconnection or loosening of a high-voltage connector, potentially exposing individuals to dangerous HV levels.
A simplified representation of HVIL is shown below. Here, it can be observed that HV connector is equipped with a “Permanent connection inside HV connector”. When the HV connector and low-voltage/signal connectors are connected to the component, the HVIL connections entering from the low-voltage/signal connector, completing the circuit through the internal permanent connection of the HV connector.
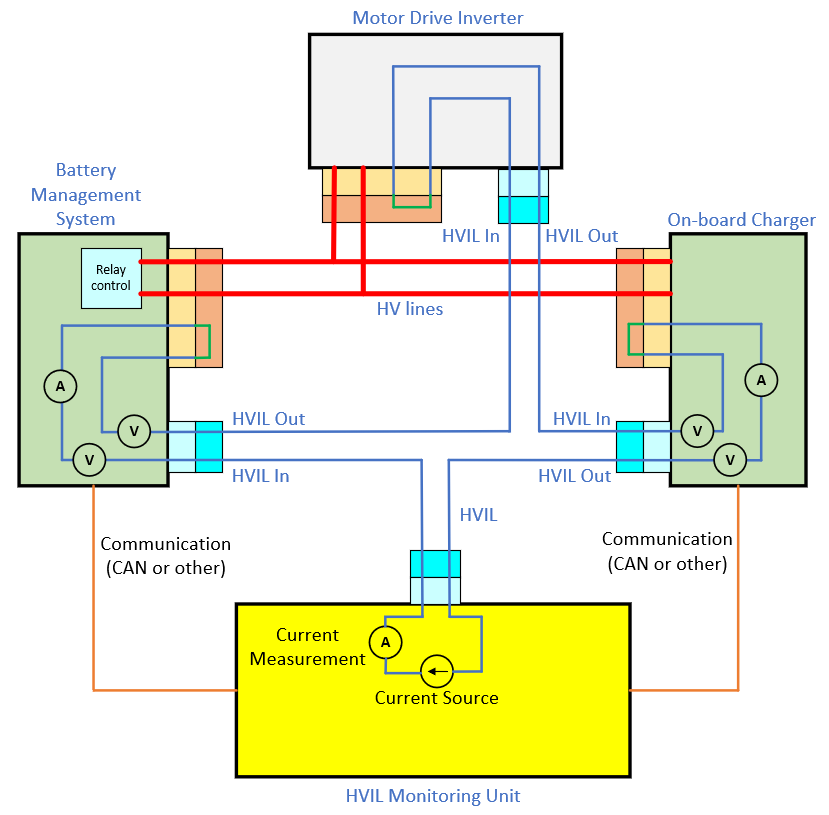

To assess the connection status of the HV connectors, the HVIL Monitoring Unit applies a predefined current (typically a few milliamperes) to the HVIL loop and measures the returning current. If the measured current matches the predefined current, it indicates that all connectors in the HV system are securely connected, and the HV can be activated safely. Conversely, if a connector is disconnected or loosely connected, resulting in a reduced measured current (or 0A), it indicates a problem with the HV connector status. Upon detecting an issue, the HVIL Monitoring Unit communicates this information to the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), which controls the HV relays (e.g., the Battery Management System in the above picture) to deactivate the HV.
Depending on the design, certain components in the HV system may possess the capability to measure HVIL parameters (current and voltages). For example, in the above picture, the Battery Management System and On-board Charger can measure HVIL parameters, whereas the Motor Drive Inverter lacks this capability.
If components are equipped to measure HVIL parameters, they can communicate the status as follows, which is beneficial for pinpointing the location of connector issues:
- If the HVIL current matches the predefined value, the HVIL system is functioning correctly.
- If the HVIL current does not match the predefined value and both ‘HVIL In’ and ‘HVIL Out’ voltages are 0V, it indicates a fault towards the components on the ‘HVIL In’ side.
- If the HVIL current does not match the predefined value and both ‘HVIL In’ and ‘HVIL Out’ voltages are above 0V, it indicates a fault towards the components on the ‘HVIL Out’ side.
- If the HVIL current is not as predefined, with ‘HVIL In’ voltage > 0V and ‘HVIL Out’ voltage at 0V, it indicates a fault within that same component.
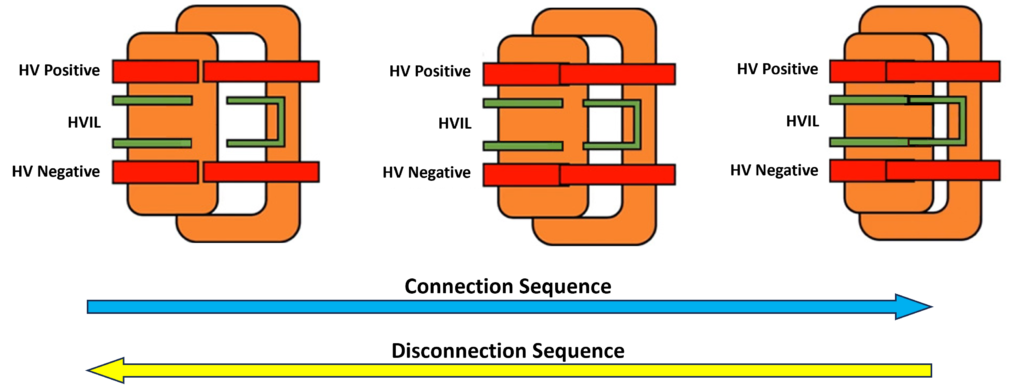
HV connector with HVIL pins:
To ensure the safe connection and disconnection of HV, HVIL pins are designed in a way to connect only after the HV pins connection during the connection process and to disconnect first during disconnection process. This ensures that as long as the HVIL pins are connected, the HV pins remain connected, maintaining safety.

Conclusion:
In conclusion, the HVIL system represents a pivotal safety feature within EVs, safeguarding individuals against the risks associated with HV components during assembly, repair, maintenance, and operation. Through its ingenious design, HVIL ensures that HV parts are only accessible when they are safely isolated, significantly reducing the danger of electrical shocks. Furthermore, the strategic design of HVIL pins ensures that HV connections are only engaged or disengaged in a sequence that prioritizes safety, maintaining an essential barrier against electrical risks.
As the automotive industry continues to shift towards electrification, the role of HVIL in ensuring the safe handling of HV systems becomes increasingly critical, highlighting its contribution to the advancement of vehicle safety technologies and the protection of individuals interacting with these systems.
EV Charging Explained – Everything you need to know about Electric Vehicle Charging