Bidirectional DC EVSE: Functional Overview
This article is a continuation of the discussion on DC EVSE, so it’s recommended to read the previous article before proceeding. This article focuses specifically on the bidirectional functional capabilities of the DC EVSE.
Abbreviations:
BPT = Bidirectional Power Transfer
EV = Electric Vehicle
EVSE = Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (Charging Station)
EVCC = Electric Vehicle Communication Controller
SECC = Supply Equipment Communication Controller
OBC = On-Board Charger
V2G = Vehicle to Grid
V2H = Vehicle to Home
V2B = Vehicle to Building
V2L = Vehicle to Load
V2V = Vehicle to Vehicle
What is a Bidirectional DC EVSE?
A Bidirectional DC EVSE enables two-way energy flow between an electric vehicle (EV) and external systems such as the power grid, homes, or other energy storage systems. Unlike traditional unidirectional DC EVSE, which only transfers power to charge an EV, bidirectional DC EVSE can both charge and discharge energy, effectively turning EVs into mobile energy storage units for applications like V2G and V2H.
How Does the Hardware Architecture Differ from Standard DC EVSE?
While bidirectional DC EVSE may appear similar to conventional DC fast chargers, its hardware design includes key modifications to enable energy export capabilities. The primary distinctions are:
1. Support for Bidirectional Power Flow
- Equipped with specialized inverters and switching mechanisms to allow seamless power transfer in both directions.
- Uses advanced power electronics, such as bidirectional AC/DC and DC/DC converters, to efficiently reverse the current flow when discharging power back to external systems.
2. Fast-Response Power Electronics
- Incorporates high-speed switching devices and intelligent controllers to dynamically adapt to fluctuating grid or load demands.
- Enables real-time synchronization with the grid during V2G or stabilizes voltage and frequency in V2H modes..
3. Intelligent Control Systems
- Features sophisticated control algorithms that optimize energy flow management, reducing conversion losses and improving efficiency.
- Ensures compliance with grid regulations and safety protocols to maintain stable operation in various bidirectional charging scenarios.
4. Integrated Backup Power Module
- Includes a low-voltage backup power supply to maintain critical system functions even during power interruptions.
Supports essential components such as the control unit and AC grid switching mechanisms, ensuring operational continuity during outages.
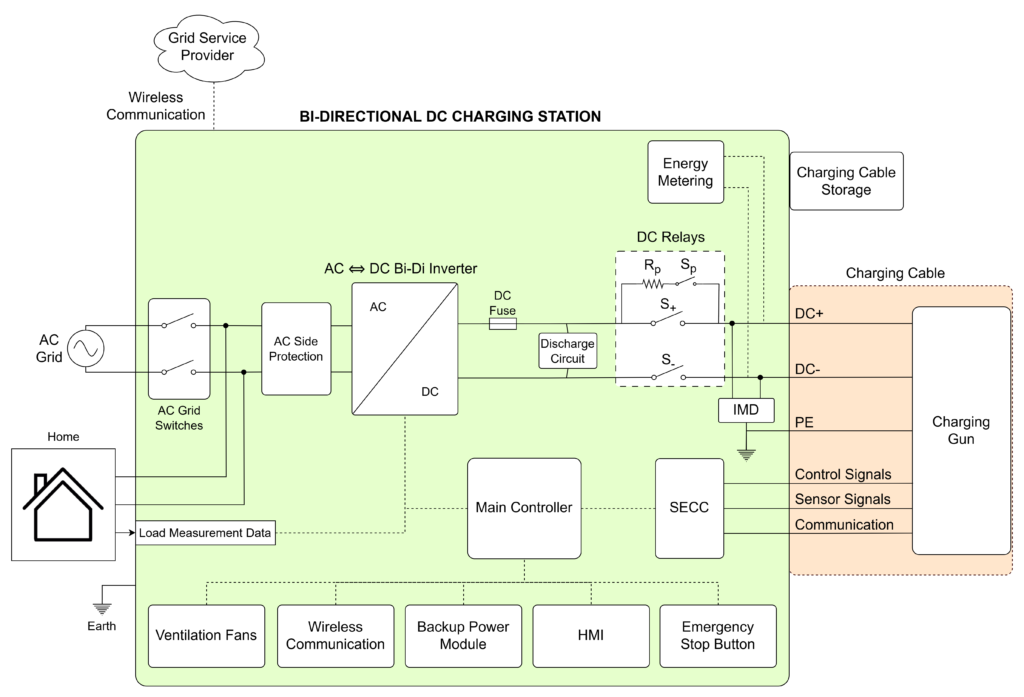
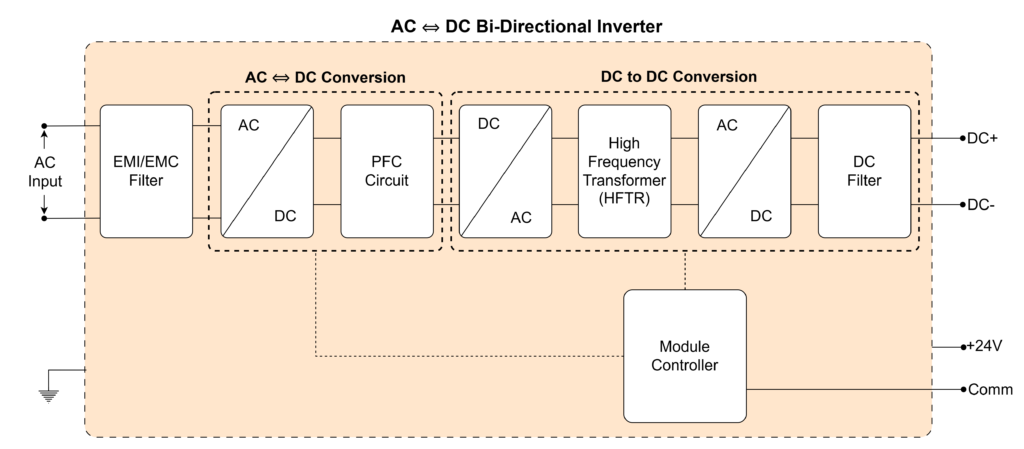
Different Modes a Bidirectional DC EVSE Should Support
Refer Bidirectional Power Transfer (BPT) or Bidirectional Charging in EVs: Overview for details.
In conclusion, Bidirectional DC EVSE transforms EVs into active energy resources, enhancing grid stability, optimizing energy costs, and promoting renewable energy integration. With its advanced hardware and control systems, it plays a crucial role in the future of smart energy ecosystems.
EV Charging Explained – Everything you need to know about Electric Vehicle Charging