Overview of Global Charging Types or Standard Connectors of EVs
Read History of EV Charging to know the evoluation of these standard connectors.
As the world shifts toward electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy solutions, the need for efficient and standardized charging infrastructure has never been greater. The rapid adoption of EVs across the globe has led to the development of various charging types and connector standards, each designed to ensure the smooth operation and compatibility of charging stations and vehicles. In this article, we will explore the different global charging types, from AC to DC fast charging, and highlight the key charging standard connectors used worldwide. By understanding these standards, we can better navigate the complexities of EV charging infrastructure and ensure that electric vehicle owners have access to reliable, universal charging solutions.
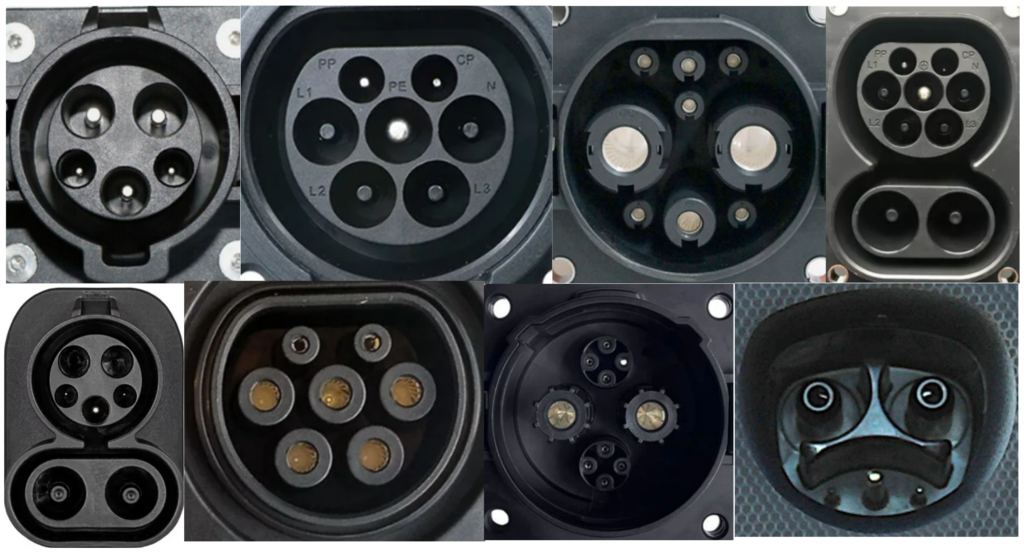

Below is the overview of global charging types:
| Charging Type | Electrical Specification | Communication Channel | Communication Standard | Geographical Usage (Dominant Use) |
| Type-1 (SAE J1772) | Supply: AC Phases: Single-phase, Voltage: Up to 240 V, Current: Up to 80 A, Power: Up to 20 kW | Control Pilot (CP) | Basic: SAE J1772, Digital communication: ISO 15118-2 | North America, Japan |
| Type-2 (IEC 62196-2) | Supply: AC Phases: Three-phase, Voltage: Up to 250 V (Phase), Current: Up to 63 A, Power: Up to 43 kW | Control Pilot (CP) | Basic: IEC 61851-1, Digital communication: ISO 15118-2 | Europe, Australia |
| CCS1 (Type-1 + DC Pins) | Supply: AC and DC Spec for AC is same as Type-1, DC Voltage: Up to 1000 V, DC Current: Up to 500 A, Power: Up to 400 kW | Control Pilot (CP) | For AC: Same as Type-1 For DC: ISO 15118-2, DIN 70121 | North America |
| CCS2 (Type-2 + DC Pins) | Supply: AC and DC Spec for AC is same as Type-2, DC Voltage: Up to 1000 V, DC Current: Up to 500 A, Power: Up to 400 kW | Control Pilot (CP) | For AC: Same as Type-2 For DC: ISO 15118-2, DIN 70121 | Europe, Asia, Australia |
| GBT AC (GB/T 20234.2) | Supply: AC Phases: Three-phase, Voltage: Up to 250 V (Phase), Current: Up to 63 A, Power: Up to 43 kW | Control Pilot (CP) | GB/T 18487.1 | China |
| GBT DC (GB/T 20234.3) | Supply: DC Voltage: Up to 1000 V, Current: Up to 250 A, Power: Up to 250 kW | CAN | GB/T 27930 | China |
| CHAdeMO | Supply: DC Voltage: Up to 1000 V, Current: Up to 400 A, Power: Up to 400 kW | CAN | CHAdeMO 2.0 | Japan |
| NACS (SAE J3400) | Supply: AC and DC (on same pins) Spec for AC is same as Type-1, DC Voltage: Up to 1000 V, DC Current: Up to 400 A, Power: Up to 400 kW | Control Pilot (CP) | For AC: Same as Type-1 For DC: ISO 15118-2, DIN 70121 | North America |
Let’s take a look at the different charging connectors below.
Read Electric Vehicle Charging Inlet (EVI): Components and Interfaces to learn more about the interfaces and components of all standard connectors.
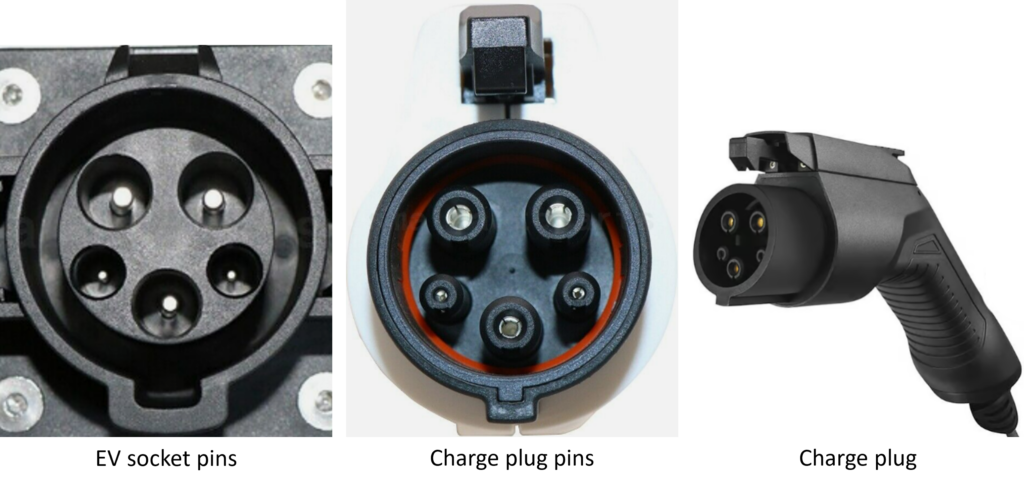
1. Type-1 (SAE J1772) – AC Connector:

2. Type-2 (IEC 62196-2) – AC Connector:

3. CCS1 (Combined Charging Standard-1) – AC & DC Connector:

4. CCS2 (Combined Charging Standard-2) – AC & DC Connector:

5. GB/T AC (GB/T 20234.2) – AC Connector:

6. GB/T DC (GB/T 20234.3) – DC Connector:
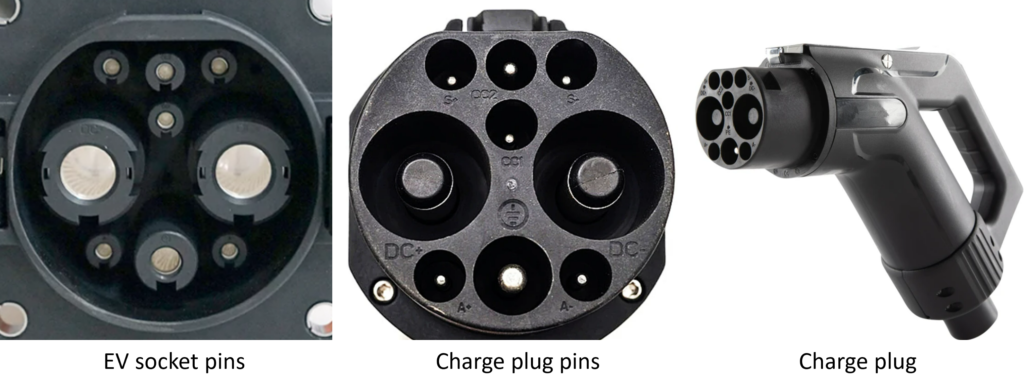
7. CHAdeMO – DC Connector:
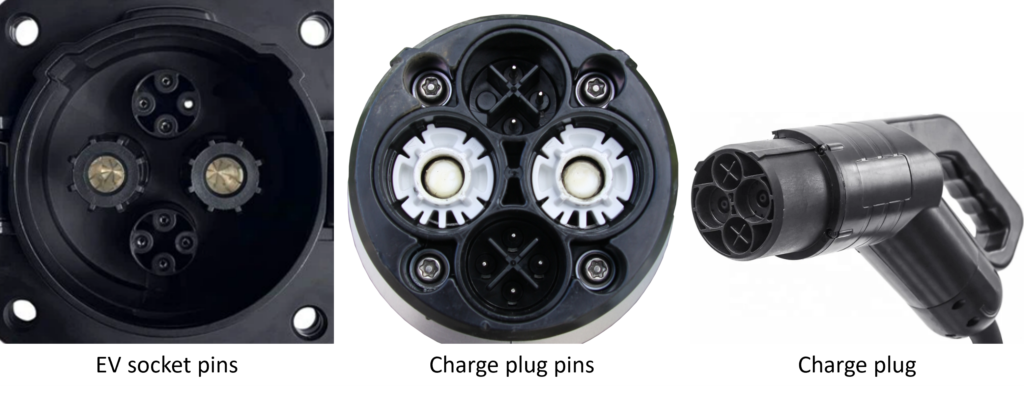
8. NACS (North American Charging Standard) – AC & DC Connector:

EV Charging Explained – Everything you need to know about Electric Vehicle Charging